Benefits of Urolithin A to the Body
Urolithin A is an intestinal metabolite of ellagic acid with antioxidant and antiproliferative effects; it inhibits the growth of T24 and Caco-2 cells with IC50 values of 43.9 and 49 μM, respectively.
|
Common name |
Urolithin A |
English name |
Urolithin A |
|
CAS |
1143-70-0 |
Molecular weight |
228.20000 |
|
Density |
1.516g/cm3 |
Boiling point |
527.9ºC at 760 mmHg |
|
Molecular formula |
C13H8O4 |
Melting point |
N/A |
|
MSDS |
N/A |
Flash point |
214.2ºC |
Physical and chemical properties of urolithin A
Urolithin A is a secondary metabolite of the natural polyphenol compound ellagitannin. The latest studies have shown that urolithin A has important biological activities, such as anti-oxidation, anti-inflammation, anti-aging, regulating estrogen/androgen and inducing mitochondrial autophagy. Therefore, urolithin A plays an important role in the prevention and treatment of many diseases, such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, diabetes, obesity, osteoarthritis, etc.
|
Density |
1.516g/cm3 |
|
Boiling point |
527.9ºC at 760 mmHg |
|
Molecular formula |
C13H8O4 |
|
Molecular weight |
228.20000 |
|
Flash point |
214.2ºC |
|
Exact mass |
228.04200 |
|
PSA |
70.67000 |
|
LogP |
2.35740 |
|
Appearance solid |
solid; White to light yellow powder to crystal |
|
Vapor pressure |
9.24E-12mmHg at 25°C |
|
Refractive index |
1.717 |
|
Storage conditions |
0-10°C; avoid heating |
Source and structural characteristics of urolithin
Urolithin A (UroA) and urolithin B (UroB) were first isolated from sheep kidney stones as metabolites of ellagic acid. Natural urolithin is not common in nature, but as a metabolite of ellagic tannin or ellagic acid, it is widely distributed in the urine, feces and bile of mammals such as humans, rats, mice, cattle and pigs. Espín et al. found that urolithin can be enriched to a high concentration in the bladder and gallbladder of Iberian pigs, but there is no obvious enrichment in other tissues such as muscle, fat, kidney, liver and heart. Experimental studies in mice and humans have found that urolithin and its derivatives are enriched in prostate tissue and are also distributed in human colon tissue.
Urolithin is produced by ellagic acid losing a lactone ring and gradually dehydroxylating it. After ellagic acid loses its lactone ring, urolithin M-5 (UroM-5) is first obtained. UroM-5 is dehydroxylated at different positions to produce several tetrahydroxy urolithin isomers such as urolithin D (UroD) and urolithin M-6 (UroM-6). Tetrahydroxy urolithin loses a hydroxyl group to produce trihydroxy urolithins such as urolithin C (UroC) and urolithin M-7 (UroM-7). Trihydroxy urolithin loses another hydroxyl group to produce dihydroxy urolithins such as UroA and urolithin A isomer (isoUroA), and finally monohydroxy urolithin B (UroB) is obtained. Moreover, isoUroA is easier to dehydroxylate to produce UroB than UroA. García-Villalba et al. It used in vitro intestinal microbial metabolism experiments to discover the metabolites of ellagic acid, UroM-5, UroM-6, UroM-7, UroC, and urolithin E (UroE), confirming for the first time that urolithin is produced under the action of intestinal flora.
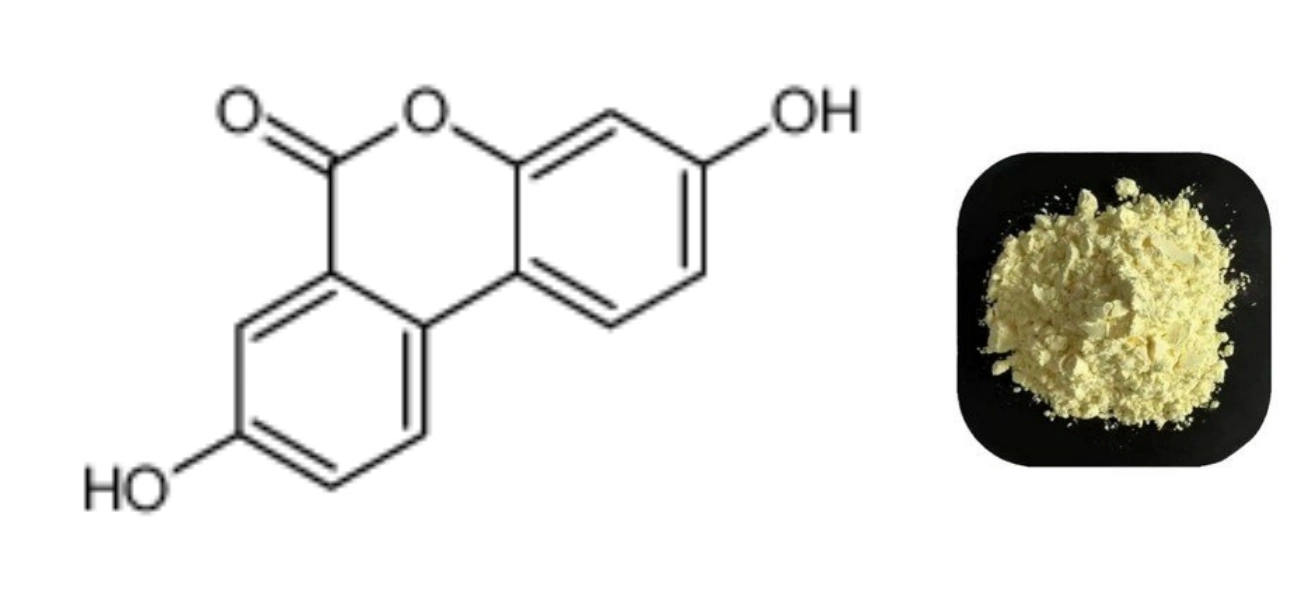
Urolithin A is a product of intestinal flora. After the human body eats vegetables and fruits such as pomegranates, berries and nuts, the intestinal bacteria and the phenolic antioxidants rich in the above fruits and vegetables react to produce urolithin A. In recent years, some preclinical studies have pointed out that urolithin A helps mitochondrial proliferation and strengthens its function, thereby promoting cell health, and the effect is particularly significant in muscles, brain, joints and other parts.
Additional benefits of urolithin A: weight loss and visceral fat
In addition, urolithin A helps lose weight. An animal experiment in 2020 showed that the research team fed overweight mice in 4 ways: normal diet, high-fat diet, high-fat diet supplemented with urolithin A after 10 weeks, and high-fat diet supplemented with urolithin B after 10 weeks. The final result was that the two groups of obese mice supplemented with urolithin had a significant decrease in weight and visceral fat.

_1730691017423.webp)












